Instructions
Instructions
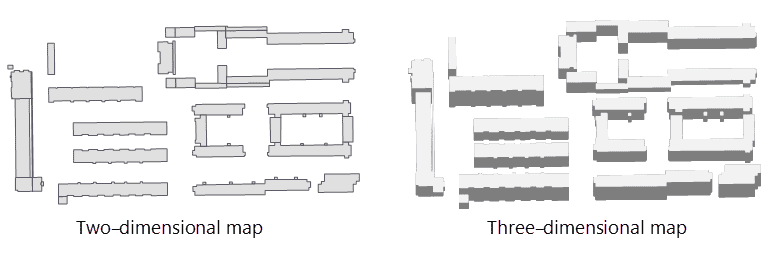
A stereoscopic map varied from a plane map is a map with the sense of volume and can help people identify surface features more easily. A stereoscopic map adds levels of a plane map. You are allowed to set styles of the topping and the shadow of a stereoscopic map to make the map beautiful.
introduces features to make a two-dimensional map have a stereoscopic effect. You are required to specify a field as the height property of the result map to generate its topping and side data.
 Basic steps
Basic steps
- Data preparation : Prepare a vector region dataset for creating a stereoscopic map and the dataset must have a field in integer or double.
- Click “Data” > “Data Processing” > “Map Making” > “Stereoscopic Map” to open the “Create 3D Map” dialog box.
- In the Input area, specify your vector region dataset and set the stretching height and the name of result data.
-
Click “OK”. The result contains two region dataset, one is the topping dataset and the other one is the side dataset.
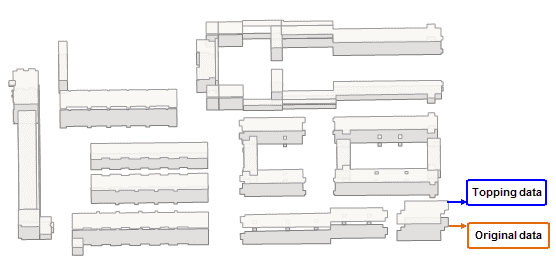
- The topping dataset
The topping dataset is generated by moving each original object a certain distance (the height of each object) along the Y axis. The result is what the following picture (the left one) shows, and because of there is no side data, the result does not have the stereoscopic effect.
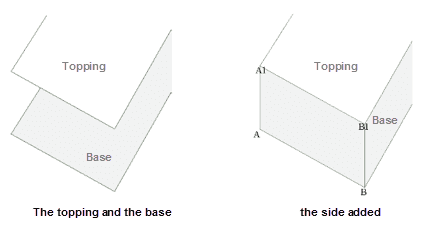
* **The side dataset**Compared to the original data, the topping data has no offset in the X axis and just offsets along the Y axis, and so we connect the first point (the point A in the following picture) of the original data to the first point of the topping data (the point A1 in the following picture) and connect the second point (the point B in the following picture) of the original data to the second point of the topping data (the point B1 in the following picture) and so on to produce the side data.
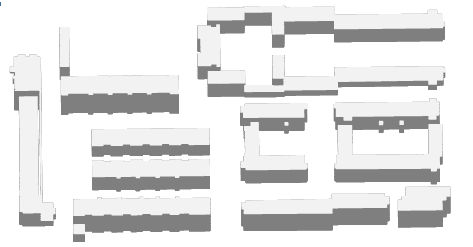
- Add the topping data and the side data into a map and then configure styles of layers to get a stereoscopic map.