 Introduction
Introduction
Redefine every pixel value of the raster dataset. The reclassification is only applicable to the raster datasets (GRID), and isn’t applicable to the image datasets (IMAGE).
Reclassify the cell values of the source raster data and assign them according to the new classification criterion. The result is that use the new values to replace the original values of the cell values. For the known raster data, in order to find out the law of cell value or facilitate the further analysis, the reclassification is very necessary. The reclassification mainly contains the following four forms:
- Use the new value to instead of the old pixel value. For example, when change the land type, assign the new cell value to the wasteland that already reclaimed to the farmland.
- Reclassify the cell values and assign the cell in the same group to the same values to simplify data. For example, the arid land, irrigable land and arable land are agricultural land.
- Reclassify the multiple raster data according to the uniform standard. For example, The influence factors of building site include soil and slope. For the soil type and slope raster data of the input data, you can reclassify according to 1-10 ranks, which is easy to further location analysis.
- Assign some cells as no value that don’t need to participate in the analysis. You can also set the no value cell as the new value.
 Basic Steps
Basic Steps
- Click the ribbon Data Processing of Data tab. Click the Reclassify button on the Raster group.to open the dialog box “Reclassify”.
- Set the reclassification value of the cell value of the raster dataset in the list. Each object corresponds to a range, including Lower Value, Upper Value and Target Value three parts. The followings will introduce the detail contents.
- Lower Value: The minimum value in the range after classified the cell value of raster dataset.
- Lower Value: The maximum value in the range after classified the cell value of raster dataset.
- Target Value: The new cell value assigned to the source cell value in the classification range.
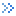 Instruction for Toolbar Button
Instruction for Toolbar Button
 Button: Click the “Select All” button to select all the records in the list box.
Button: Click the “Select All” button to select all the records in the list box. Button: Click the “Select Inverse” button to inverse the records in the list box.
Button: Click the “Select Inverse” button to inverse the records in the list box.  Button: Click “Union Rows” to merge the multiple continuous records into a new record. The range min is the minimum cell value of the original records and the range max is the maximum cell value of the maximum cell value. When only one record is selected or multiple discrete records are selected, this function is unavailable.
Button: Click “Union Rows” to merge the multiple continuous records into a new record. The range min is the minimum cell value of the original records and the range max is the maximum cell value of the maximum cell value. When only one record is selected or multiple discrete records are selected, this function is unavailable. Button: Click the “Split Row” button to split a selected record into two new records. The cell value of the original record is split into two and be assigned into the new records. When there multiple records in the list are selected, this function is unavailable.
Button: Click the “Split Row” button to split a selected record into two new records. The cell value of the original record is split into two and be assigned into the new records. When there multiple records in the list are selected, this function is unavailable. Button: Click “Import XML File” to import the reclassification configuration file in the format of *.xml into the dialog box. You can reclassify the selected raster dataset according to the existing parameters.
Button: Click “Import XML File” to import the reclassification configuration file in the format of *.xml into the dialog box. You can reclassify the selected raster dataset according to the existing parameters. Button: Click the “Export XML File” button. You can save the reclassification settings and the related parameters in the format of *.xml format, which is easy to reuse.
Button: Click the “Export XML File” button. You can save the reclassification settings and the related parameters in the format of *.xml format, which is easy to reuse. Button: Click “Inverse Target Values” to assign the new cell value inversely.
Button: Click “Inverse Target Values” to assign the new cell value inversely.
 Export the File Structure
Export the File Structure
 Copy
Copy
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<SmXml:ReclassMappingTable xmlns:SmXml="http://www.supermap.com/xml">
<SmXml:ReclassType> 2 </SmXml:ReclassType>
<SmXml:SegmentCount count="5">
<SmXml:Range1> 1348.000000 -- 1733.400000: 5.000000-1 </SmXml:Range1>
<SmXml:Range2> 1733.400000 -- 2118.800000: 4.000000-1 </SmXml:Range2>
<SmXml:Range3> 2118.800000 -- 2504.200000: 3.000000-1 </SmXml:Range3>
<SmXml:Range4> 2504.200000 -- 2889.600000: 2.000000-1 </SmXml:Range4>
<SmXml:Range5> 2889.600000 -- 3275.000000: 1.000000-1 </SmXml:Range5>
</SmXml:SegmentCount>
<SmXml:RetainMissingValue> 1 </SmXml:RetainMissingValue>
<SmXml:RetainNoValue> 1 </SmXml:RetainNoValue>
<SmXml:ChangeMissingValueTo>0.000000 </SmXml:ChangeMissingValueTo>
<SmXml:ChangeNoValueTo> -9999.000000</SmXml:ChangeNoValueTo>
</SmXml:ReclassMappingTable>- Set the source data.
- Datasource: List all the datasources in current workspace and select the datasources that the datasets needed to reclassify belong to.
- Dataset: List all the grid datasets (GRID) in the current datasource. Select the datasets that need to reclassify in the list. Here it will locate to the selected datasets in the workspace manager.
- Set the result data.
- Datasource: List all the datasources in current workspace and select the datasource that contains the result datasets. It is the same with source datasource by default.
- Dataset: Set the name of the result dataset.
- Pixel Format: Set the pixel format of the result dataset. The system provides integer, long integer, single precision float and double precision float. See Pixel Type of Grid Dataset for more information about pixel format.
- Set the status of closed and open. The open interval means that the border value isn’t included in the interval range and closed interval means that the border value is included in the interval range.
- [L,R): Specify that the left border is in the interval range and the right is out of the interval range.
- (L,R]: Specify that the left border is in out of the interval range and the right is in the interval range.
- Set the class settings.
- Ranges: Determine the ranges and the default is 10. After inputting the ranges, the system will calculate every ranges with the arithmetic mode according to minimum and maximum values in the raster data. For example, the minimum value is 200 and the maximum value is 1000 in the raster dataset. The input range is 4, so the value of each range are 200, 400, 600, 800 and 1000.
- Interval: Determine every segment value according to the interval. After input the interval, the system will segment and increase until to the maximum value according to the interval. The final value should be less than or equal to the maximum. For example, in the raster datasets, if the interval is set to 200, the segment values are 200, 400, 600, 800 and 1000; If the interval is set to 300, the segment values are 200, 500 and 800.
- Set the custom target value.
- NoValue: For the no value in the raster dataset, you can keep the no value status or set a new cell value.
- Unclassified: The unclassified is the unrelated cell values in the left list. You can set a new cell value uniformly.
- Click “Environment Settings” button to open the “Environment Setting for Raster Analysis” where you can set the analysis parameters to values as needed. For detail operations, please refer to Setting the Analysis Environment.
Note: you are allowed to specify the environment parameters as global variables, then you do not need to set the parameters again in other operations. Also the system can read parameter values specified in the raster analysis environment if you do not set parameters here.
- After finished the parameter settings, click “OK” button to execute raster reclassify operation.