Projection
The earth is a sphere, its surface is composed of curved surfaces, but usually we need to draw the map in the plane drawings, so it’s needed to convert it to plane surfaces. We must adopt special methods to spread the curved surface, make it a plane without cracking or fold, hence there is the theory of map projection and projection method. The basic principle is: the position of the point on the sphere is decided by its latitude and longitude, so in a projection, first draw the intersection points of the latitude and longitude lines on the planar, then the connected line by the same longitude value becomes the longitude line; the connected line by the same latitude value becomes the latitude line, and then each point on the sphere can get its corresponding position on the planar as shown below.
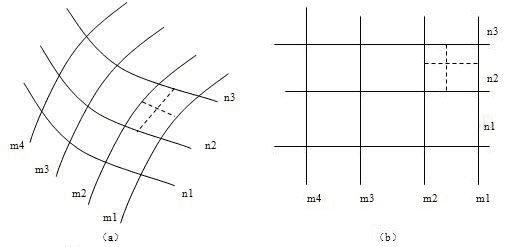
Fig: Convert the Point on the Sphere to the Planar
Principle of Projection
Many analysis technologies and spatial data are based on 2D coordinates, which needs to store the spatial coordinates in 2D planar way, so we often need to convert the data from 3D to 2D. The map projection method is to convert the latitude/longitude coordinates (?,f) to the planar coordinates (X,Y). When converting the coordinates from 3D to 2D, it may have distortion, the map projection is designed to reduce the distortion.
In a word, the map projection is to ensure the connectivity and completeness of the data when converting from 3D to 2D, which is the basic requirement of mapping, also is necessary for the spatial operation and spatial analysis. Map projection is very important for GIS applications.
Methods of Projection
There are two kinds of projection method, namely geometric perspective analysis and mathematical method
- Geometric perspective analysis method
It uses the perspective relations between the objects, to project the points on the earth surface to the projected planar such as plane, cylindrical surface, conical surface, as shown below:
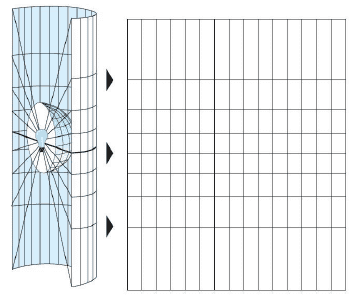
Fig: Geometric Perspective Analysis Method
- Mathematical method
It defines the functional relationship between the geographic coordinates and the planar coordinates. Currently most projections use this method.
Distortion of Projection
The earth ellipsoid is a non extensible surface, but the map is a planar. When converting the ellipsoid surface to a planar, it will cause rupture or overlap of some parts so as to make the features and terrain in this part to not consistent or complete, which should be stretched or compressed to reduce rupture or overlap. While stretching or compressing, it will get different from the original shape, which is called distortion.
The deformation of the map includes: length deformation, angular deformation, area deformation and shape deformation.
- Length deformation
The length deformation is the difference between the length ratio and 1, and the length ratio is the length of a small line on the projection plane : the corresponding small line length on the ellipsoidal surface. The length deformation is used to reflect the degree of the change of the line projection, which is the most basic deformation on all projections.
- Angular deformation
The angular deformation is the difference between the angle of the two direction lines on the projection plane and the angle of the corresponding lines on the ellipsoid surface. Angular deformation is a specific sign of shape deformation.
- Area deformation
The area deformation is the difference between the area ratio and 1, and the area ratio is the ratio of the small area on the projection surface to the small area on the ellipsoidal surface. Area deformation is a quantitative index to measure the size of map projection deformation
- Shape deformation
Shape deformation is the difference between the shape on the planar map and the corresponding shape on the globe.